Digital electronics are those electronics systems that use a digital signal instead of an analog signal. Digital electronics are the most common representation of Boolean algebra and are the basis of all digital circuits.In digital electronics all values are expressed in terms of 0's and 1's combination.
Electronics Guide
Tuesday, September 1, 2015
Thursday, July 23, 2015
working of amplifier
Single Stage RC Coupled CE Amplifier
The figure shows a single stage CE amplifier. C1 and C3 are coupling capacitors, they are used for blocking the dc component and passing only ac part they also ensure that the dc basing conditions of the BJT remains unchanged even after input is applied. C2 is the bypass capacitor which increases the voltage gain and bypasses the R4 resistor for ac signals. The BJT is biased in the active region using the necessary biasing components. The Q point is made stable in the active region of the transistor. When input is applied as shown below the base current starts to vary up and down, hence collector current also varies as IC = β × IB. Therefore voltage across R3 varies as the collector current is passing through it. Voltage across R3 is the amplified one and is 180° apart from the input signal. Thus voltage across R3 is coupled to the load and amplification has taken place. If the Q point is maintained to be at the centre of the load very less or no waveform distortion will take place. The voltage as well as current gain of the CE amplifier is high (gain is the factor by which the voltage of current increases from input to output). It is commonly used in radios and as low frequency voltage amplifier.
The BJT is biased in the active region using the necessary biasing components. The Q point is made stable in the active region of the transistor. When input is applied as shown below the base current starts to vary up and down, hence collector current also varies as IC = β × IB. Therefore voltage across R3 varies as the collector current is passing through it. Voltage across R3 is the amplified one and is 180° apart from the input signal. Thus voltage across R3 is coupled to the load and amplification has taken place. If the Q point is maintained to be at the centre of the load very less or no waveform distortion will take place. The voltage as well as current gain of the CE amplifier is high (gain is the factor by which the voltage of current increases from input to output). It is commonly used in radios and as low frequency voltage amplifier.
To further increase the gain multistage amplifiers are used. They are connected via capacitor, electrical transformer, R-L or directly coupled depending on the application. The overall gain is the product of gains of individual stages. Figure below shows a two stage CE amplifier. various parameters of CE amplifier are
| Definition | Expression (with emitter degeneration) | Expression (without emitter degeneration, i.e., RE = 0) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current gain |  |  | 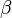 |
| Voltage gain |  |  |  |
| Input impedance |  |  |  |
| Output impedance |  |  |  |
types of transistor amplifier
1. common Emitter amplifier
2. common Base amplifier
3. common Collector amplifier
2. common Base amplifier
3. common Collector amplifier
COMMON-COLLECTOR CONFIGURATION
COMMON-BASE CONFIGURATION
COMMON-EMITTER CONFIGURATION
Advantages and Disadvantages of transistor amplifier
Advantages of CE amplifier:
- A common emitter amplifier is inverting and has low input impedance
- high output impedance
- high voltage gain
- high current gain.
Disadvantages of CE amplifier:
- 1. It has a high output resistance.
- 2. It responds poorly to high frequencies.
- 3. It has high thermal instabilities.
- 4. It's voltage gain is very unstable.
Advantages of CB amplifier:
- decent voltage amplifier, and current in is about equal to current out (actually current in is slightly greater than current out).
- The common base circuit works best as a current buffer. It can take an input current at a low input impedance, and deliver nearly that same current to a higher impedance output.
Disadvantages of CB amplifier:
- It requires two DC power sources to run this type of circuit.
- Measure another voltage between emitter (input) and Collector(output).
- Compare voltage between Emitter and Base to see it is within the limit of transistor.
- Common Base circuit mostly use on OSC circuit or matching circuit. It has less gain than CE type.
- amplification factor of common base amplifier is less less than common emitter amplifier.
Advantages of CC amplifier:
- It has current gain but maintain voltage gain unchanged
- It has the lowest output impedance compare to other type amplifier
- It can be used for impedance matching between an amplifier stage with a high output impedance and an amplifier stage with a low input impedance.
- When used like this it is sometimes called a buffer amp or isolation amp.
- When placed between the the two stages it prevents the stage with the low input impedance from overloading the stage with the high output impedance.
- The Voltage gain of a common collector amp is at best slightly less than 1
COMPARISON AMONG DIFFERENT TYPES OF AMPLIFIER:
| Common Emitter | Common Collector | Common Base | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Gain | Medium | Low | High |
| Current Gain | Medium | High | Low |
| Input Impedance | Medium | High | Low |
| Output Impedance | Medium | Low | High |
Sunday, July 19, 2015
Application of network theorem
- Both the methods are used to solve the complex network.
- Norton's Theorem & Thevenin's Theorem are "Duals".
- substitution theorem can be used in both linear and nonlinear circuits. For those nonlinear circuits that have a unique solution, we can use the substitution theorem in the equivalent transformation.
- they can be applied to both ac and dc source.
- For easy detemination of circuit parameter
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



